Light
What is light?

There are several ways to think of light. The classical description says light is an electro-magnetic wave. This means that it is a varying electric and magnetic field, which spreads out or propagates from one place to another. It is not a physical substance.
The modern quantum mechanical description says that light can also be considered to be particles called photons. These carry energy and momentum but have no mass. In both descriptions, the light energy is carried by a very real and observable mechanism, which is not a physical object.
A more inclusive definition includes any radiation, which shares with visible light many of the properties such as reflection, refraction, polarization, diffraction and velocity, e.g., ultra-violet and infra-red "light" which are of course invisible to humans though bees and butterflies have well developed ultra-violet vision. The term electromagnetic radiation refers to all the types of radiation that resemble light and can be characterized by frequency and wavelength and these are, in order of increasing wavelength, cosmic rays, g-rays, X-rays, ultra-violet light, visible light, infra-red radiation, microwaves, and radio waves.
How does light travel?
Light moves in waves. How big those waves are determines what type and color of light it is. Those waves, however, are so small that they appear to be straight lines.
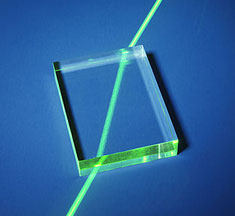
Light moves in straight lines only when it's not moving through anything at all (ie. in a vacuum). When it moves through air, water, glass, or anything else, its behavior changes. There are two main things that happen to change the direction of the light's motion:
1. Reflection: Reflection is what happens when light bounces off of something. This is what we see when we look in the mirror. This is also what we see when we look at anything around us. In order to reach your eyes, light bounces off of the object that we're looking at, changing its direction. It can also bounce off of particles (like water) in the air, which is why we may be able to see beams of sunlight on a foggy day.
2. Refraction: Refraction is what happens when light passes from one medium (one type of stuff) into another. When this happens, the light will actually bend. (Actually, it usually splits in two - some of it reflects off the surface, and some of it keeps going through.) The light that goes through bends at the surface. The angle that it bends at depends on what the two mediums are. For example, light will bend a different amount when it goes from air into glass than it does when it goes from air into water.