Guyana
Country statistics
Land area: 76,004 sq miles (196,850 sq km)
Total area: 83,000 sq miles (214,970 sq km)
Population (2012 est.): 741,908 (growth rate: -0.327%); birth rate: 16.69/1000; infant mortality rate: 35.59/1000; life expectancy: 67.39
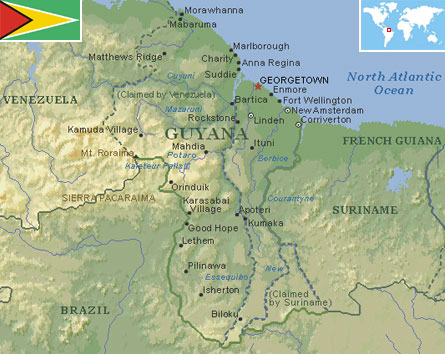
Capital City: Georgetown
Monetary unit: Guyanese dollar
Languages: English (official), Amerindian dialects, Creole, Caribbean Hindustani (a dialect of Hindi), Urdu
Ethnicity/race: East Indian 43.5%, black (African) 30.2%, mixed 16.7%, Amerindian 9.1%, other 0.5% (2002 census)
Religions: Protestant 30.5% (Pentecostal 16.9%, Anglican 6.9%, Seventh-Day Adventist 5%, Methodist 1.7%), Hindu 28.4%, Roman Catholic 8.1%, Jehovah's Witnesses 1.1%, Muslim 7.2%, other Christian 17.7%, other 4.3%, none 4.3% (2002 census)
Country introduction

Guyana is located in the northern coast of South America and is bordered to the east by Suriname, to the south and south-west by Brazil, to the west by Venezuela, and on the north by the Atlantic Ocean. It was a former colony of the Dutch and, for over 200 years, the British.
The coastal plain, a narrow and fertile marshy plain along the Atlantic coast, occupies about 5% of the country's area and is home to more than 90% of its inhabitants. Here major cash crops, sugar, and a major subsistence crop, rice is grown. More than 25% of the population lives in or near the capital of Georgetown.
Moving south inland from the coastal plain presents a white sand belt. This area is 150 to 250 km (93 to 155 miles) wide and consists of low sandy hills interspersed with rocky outcroppings. The white sands support a dense hardwood forest. These sands cannot support crops, and if the trees are removed erosion is rapid and severe. Most of Guyana's reserves of bauxite, gold, and diamonds are found in this region.
The interior highlands in the south, is the largest region that consists of a series of plateaus, flat-topped mountains, and savannahs that extend from the white sand belt to the country's southern borders. The Pacaraima Mountains dominate the western part of the interior highlands. In this region are found some of the oldest sedimentary rocks in the Western Hemisphere. Mount Roraima, on the Venezuelan border and a part of the Pakaraima range is Guyana's tallest mountain at 2,762 m (9,061 ft). Much of the interior highlands consist of grassland. The largest expanse of grassland, the Rupununi Savannah, covers about 15,000 sq km (9,320 sq miles) in Southern Guyana. This savannah also extends far into Venezuela and Brazil.
The four longest rivers are the Essequibo at 1,010 km (628 miles) long, the Courantyne River at 724 km (450 miles), the Berbice at 595 km (370 miles), and the Demerara at 346 km (215 miles). The Corentyne river forms the border with Suriname. At the mouth of the Essequibo are several large islands, including the 145 km (90 miles) wide, Shell Beach. The beach lies along the north-west coast and is a major breeding area for sea turtles (mainly Leatherbacks) and other wildlife.
The culture

The culture of Guyana is a fusion of diverse color and shades, and reflects the influences of African, Indian and Nepalese, Amerindian, Chinese, Spanish, Portuguese, Dutch and British cultures. The greatest influences came from the Europeans because the Dutch managed to be the first to seize the country and take control and the British made a move in the 18th century, painting the history with the English language and membership to the British Empire. As a result of this, the country's architecture was greatly influenced by the British rulers and reflected that of British establishments.
The country's music was largely influenced by Indian and African natives, with a hint of European elements. The music that people listen to is a mixture of Caribbean, Indian, African, European, and American styles. Some of the popular tunes can be categorized under reggae, calypso, and chutney. The tunes with European influences are largely classified under Latin style. Sports are an important part of recreation with cricket being the national sport. However, soccer and basketball are also very popular.
The citizens of modern Guyana are very diverse and consists of many religions, but the main religion remains to be Christianity, Hinduism, and Islam. Universally, family life is very important in Guyanese culture. The extended family plays a major role in daily lives, and often everyone will eat together and meet for large family reunions.
Chicken, fish, and turkey dishes are very popular, with rice being a daily staple of their diet. The country's national dish is pepper pot, a stew which contains meat, spices, and a sauce called cassareep. Another popular dish is metemgie, a thick coconut based soup. Daal, a yellow split lentil is considered a special treat and can be cooked into many delicious dishes. Guyanese people also eat a lot of fresh greens, which are usually grown in rural areas. Farming is an important part of the Guyanese economy.
Clay pottery, nibbee straw hats, carvings made out of latex of the Balata tree, gold and silver jewelry are some of the traditional crafts of Guyana.
Attractions & landmarks

The most impressive attractions of Guyana are the waterfalls. Kaieteur Falls symbolises the majestic natural heritage of the country and is one of the most spectacular waterfalls in the world. It has a height of 226 m (741 ft) and is surrounded by a pristine and un-spoiled rainforest. There are several other outstanding world-class waterfalls such as Kamarang Great Falls, Kumerau Falls and Oshi Falls.
Georgetown, the capital city of Guyana located 241 km (150 miles) north-east from Kaieteur Falls, is a friendly and cultured city with a colorful mix of English heritage, Caribbean warmth and Asian influence. At the district's heart is Stabroek Market, a massive, bazaar built partly over the busy river. From the vicinity of Stabroek, the main streets that run north to the Atlantic is lined by many of the city's finest buildings that include the High Courts and City Hall, the residences of the president and the prime minister. In front of the courts stands a statue of Queen Victoria, a tribute to Guyana's British ancestry. Located a few yards up the promenade from City Hall is the pride of Georgetown, a glorious view of St. George's Cathedral, one of the tallest wooden churches in the world that stands at a height of 43.5 m (142 ft). The Georgetown Botanical Gardens is one of the treasures of the city, and is worth a visit to see the vast array of tropical flowers, fruits, and plants laid out on 185 acres of land. The gardens also has a zoo which includes a variety of species such as birds and fishes.
There is no shortage of beaches in Guyana. Shell Beach, at 140 km long (86 miles) is renowned for consisting of pure shells, a very high biological diversity and importantly for being the nesting site of 8 species of sea turtles. Another notable beach to look at include 63 Beach Berbice. The beach stretches for 10 miles, connecting several villages along the Corentyne River as it approaches the coast and includes activities such as swimming, beach volleyball and fishing.
Guyana boasts a number of resorts where an intimate experience with nature can be had. Emerald Tower rainforest Lodge on the Madewini Creek is ideal for those who are looking to relax peacefully whilst enjoying the breathtaking views. Other resorts include the Shanklands Resort that overlooks the Essequibo river. Baganara Island Resort, also on the Essequibo river about 50 miles in the interior from the Atlantic Ocean, is in a secluded location in the middle of a jungle that offers plenty of activities such as swimming and kayaking, along with organized excursions in the surrounding areas such as Marshall falls and Parrot Island.