Malaysia
Country statistics
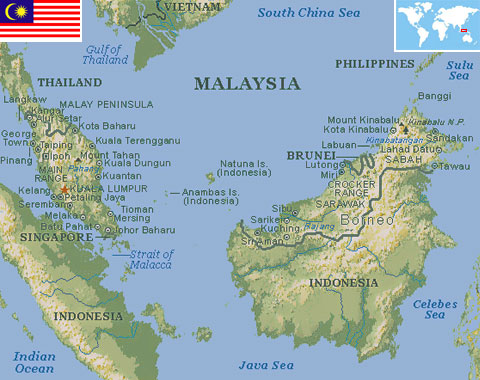
Land area: 126,853 sq miles (328,549 sq km)
Total area: 127,317 sq miles (329,750 sq km)
Population (2010 est.): 26,160,256 (growth rate: 1.7%); birth rate: 22.0/1000; infant mortality rate: 15.3/1000; life expectancy: 73.5; density per sq km: 76
Capital City: Kuala Lumpur
Monetary unit: Ringgit
Languages: Bahasa Melayu (Malay, official), English, Chinese dialects (Cantonese, Mandarin, Hokkien, Hakka, Hainan, Foochow), Tamil, Telugu, Malayalam, Panjabi, Thai; several indigenous languages (including Iban, Kadazan) in East Malaysia
Ethnicity/race: Malay and other indigenous 58%, Chinese 24%, Indian 8%, others 10% (2000)
Religions: Muslim, Buddhist, Daoist, Hindu, Christian, Sikh; Shamanism (East Malaysia)
Country introduction

Malaysia have fervently embraced modern technology. It boasts one of the world's tallest skyscrapers, the Petronas Tower and a huge cyber center for computer businesses. But it still has some of the world's most remote jungle (in Sabah and Sarawak), one of South-east Asia's most vibrant old ports (Georgetown) and an atmospheric colonial hill station (the Cameron Highlands).
Even in Kuala Lumpur, the capital, which bristles with ambitious new building projects, exotic markets and plenty of local color can still be found. As a result, travelers to Malaysia can easily ratchet up or down the levels of adventure and comfort they want to experience.
The culture

Malaysia is a multi-racial country with a rich cultural heritage. The base of the national culture is Malay culture, which is native to this region. Islamic values are embedded in Malay Culture.
As Malaysian respect each other's beliefs and faiths, cultural and religious festivals such as Hari Raya, Chinese New Year, Deepavali, Christmas, Gawai Day and other auspicious occasions are given due importance. Malaysia reflects different cultural traditions, including those of China, India, the Middle East, Europe, and the entire Malay Archipelago. Early Malay empires absorbed Indian influences, such as Hindu epics and the Sanskrit language.
Attractions & landmarks

Malaysia was under Colonial rule for many, many years and as such the old buildings reflect the influence of British architecture. This can be seen mainly in Penang.
The architecture in Malaysia is very varied, ranging from very old colonial buildings to very modern highrise buildings. If visitors travel along the countryside, a lot of Malay houses will be seen. They are mainly seen in villages or 'kampong' in Bahasa Malaysia, and are built with stilts and have large windows. This is mainly to keep the building cool and the stilts elevate the building to keep them away from floods. Kampong houses are detached houses and they usually have no fences around them.
The landmark of Malaysia is undoubtedly the Petronas Tower, which sours to a height of 452 m (1,482 ft), making it one of the highest buildings in the world. Each tower's floor plan forms an eight-pointed star, a design inspired by traditional Malaysian Islamic patterns. The 88-story towers, joined by a flexible skybridge on the 42nd floor, have been described as two 'cosmic pillars' spiraling endlessly towards the heavens.